Welcome to the second article in my series on AutoCorrect. Last time, we learned what AutoCorrect does (automatically changes words you type or spell incorrectly to their correct forms, e.g. changing “teh” to “the”) and where to find it in Words 2003, 2007 and 2010, and we can also set up a shortcut button to make it more accessible.
Now we’re going to look at how you can use AutoCorrect to speed up your typing and make it more efficient, and how you actually amend the AutoCorrect entries to tailor them to your requirements.
Why would I use AutoCorrect?
Apart from correcting common typos, AutoCorrect has two very handy uses: I use it in these ways all the time, and if you, you will save yourself time and effort.
- If there is a word you can never remember how to spell, set up a short cut AutoCorrect, just type in the first few letters, and AutoCorrect will auto complete it for you. No more finding it in the spell checker yet again. Type in Kaz and Word will display Kazakhstan.
- If there is a long word or particularly a phrase that you use over and over again – “Creative and Marketing Director”, “economic forecasting”, “qualitative and quantitative research methodologies”, set up a short cut for each one and save all that typing (and possible typos). Type cmd, ef or qq and watch the phrases type themselves!
How do I tailor AutoCorrect to my individual requirements?
The key to this is in the AutoCorrect menu we met last time.

First of all, there are some useful features on the screen directly in front of you. Here’s how you turn on and off all those useful features that sort out typing errors as you go (we’ve all typed THe at the beginning of a sentence, haven’t we). You just untick the box if you don’t want it to do something. By the way, we’ll be looking at those other tabs along the top, especially AutoFormat As You Type, in another article.

So, for now, we’re working with the standard AutoCorrect. We’ve started off with a list of signs and symbols, because they come before “A” in Word’s alphabet. To see what else there is, try typing a letter into the top, blank fields. Here we have a mixture of the standard AutoCorrect entries (abouta changes to about, etc.) but the top two are my own additional entries. See how many keystrokes and how much time I save by typing aaa and getting accountability agent application inserted into my document (plus it’s typed correctly first time!).

How to add a new entry to AutoCorrect
Let’s look at how to add those new, personalised AutoCorrect entries. Well, it’s pretty simple. Type the abbreviation or mis-spelling in the left hand column (or field), the text that you want to appear in the document in the right hand field (or highlight the word you want to add an entry for in your document, then access this menu), and press Add.
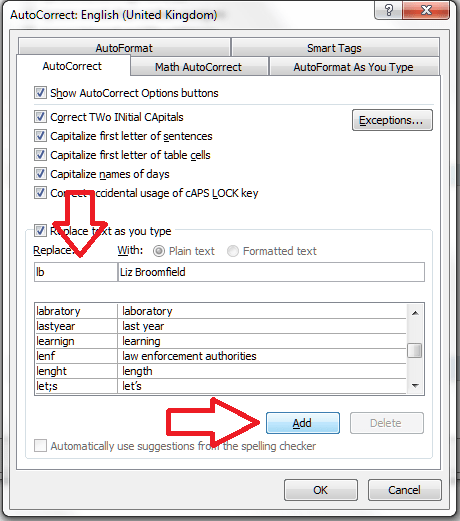
You can see that your entry has now appeared on the AutoCorrect list, in its place in the alphabetical order. Now, whenever you type lb, the words Liz Broomfield will appear in your document.

How to delete an AutoCorrect entry
What if you want to delete an AutoCorrect entry? I did this recently – I had set re to AutoCorrect to recognize for a document I was working on that had no contractions (they’re, etc.). Of course, when I was then typing something more informal, I got lots of they’recognize as it tried to do what I’d asked it to do. So I wanted to get rid of that entry altogether. Here’s how you do that: Look up the entry by typing in your abbreviation – what you type as opposed to what you want to come up. When you’ve found the one you want to delete, press the Delete button.

Now you can see that the entry for lb/Liz Broomfield has disappeared and the list goes from lastyear to learnign. Note: it doesn’t ask you if you’re sure you want to delete, but it does leave that entry in the top text fields, so if you’ve made a mistake, you can just add it again.

How to change or replace an AutoCorrect entry
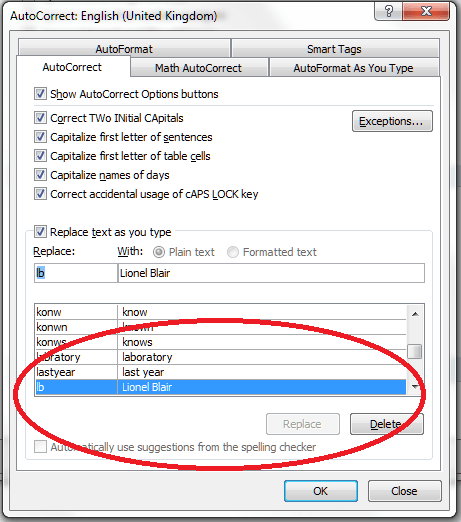
You may want to change an AutoCorrect entry – for example, you’re stopping talking about Liz Broomfield and want to refer to Lionel Blair. Type in your abbreviation and your new version of what you want Word to insert, in this case Lionel Blair. AutoCorrect will find the original entry and highlight it. The Replace button will appear – so press that.

Word does like to make sure you mean to do it when you change something, so you’ll get another little dialogue box asking if you do want to redefine this AutoCorrect entry. Press Yes (if you do).

and there you go: Liz Broomfield has changed into Lionel Blair.
Today we’ve learned why to use AutoCorrect and how to personalise it to help you type efficiently. If you’ve found this article helpful, please leave a comment or click one of the “like” buttons below! Thank you,
Please note, these hints work with versions of Microsoft Word currently in use – Word 2003, Word 2007 and Word 2010, all for PC. Mac compatible versions of Word should have similar options. Always save a copy of your document before manipulating it. I bear no responsibility for any pickles you might get yourself into!
This is part of my series on how to avoid time-consuming “short cuts” and use Word in the right way to maximise your time and improve the look of your documents. Find all the short cuts here …
 Of course this one comes under the “these words sound the same! Which on earth do I use?” category, as so many Troublesome Pairs do. What do you do if you’ve only heard the words spoken but want to write one of them (well, you look here or in a dictionary, but you know what I mean …).
Of course this one comes under the “these words sound the same! Which on earth do I use?” category, as so many Troublesome Pairs do. What do you do if you’ve only heard the words spoken but want to write one of them (well, you look here or in a dictionary, but you know what I mean …).