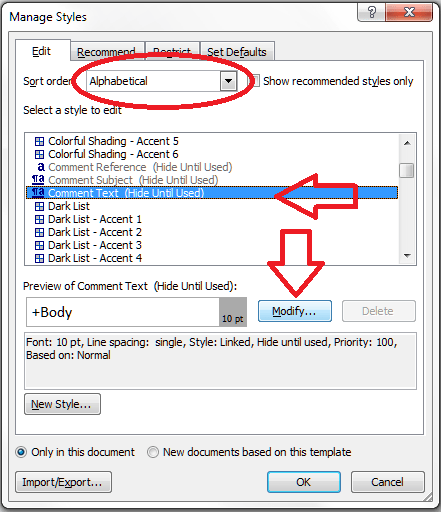
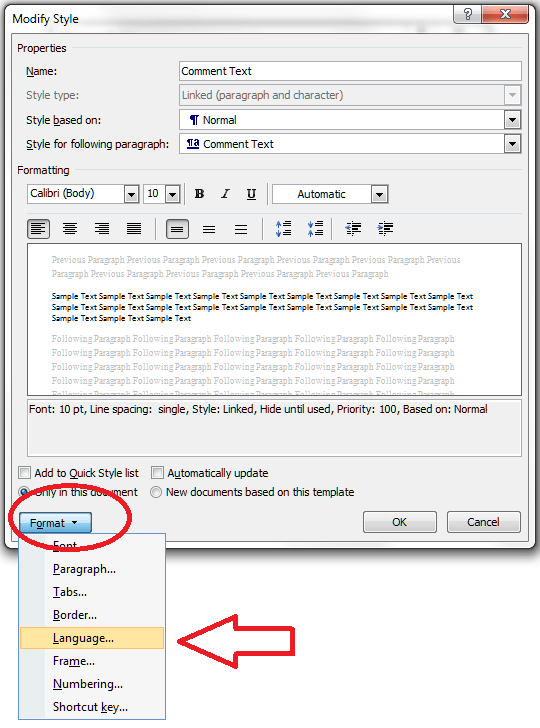
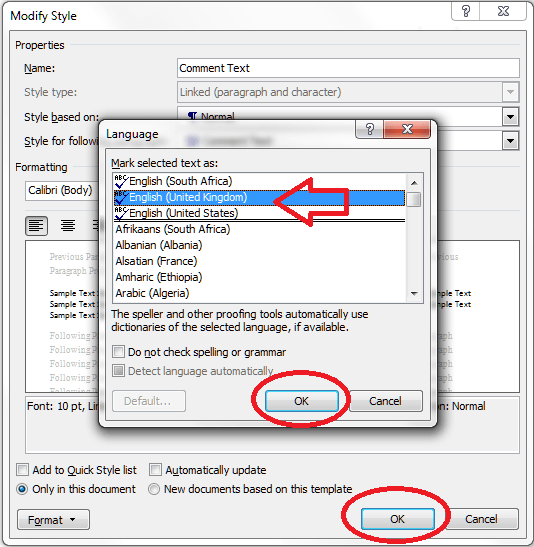
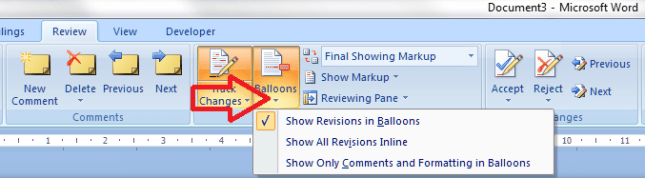
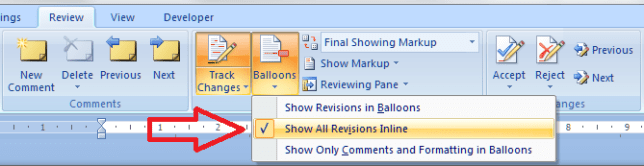
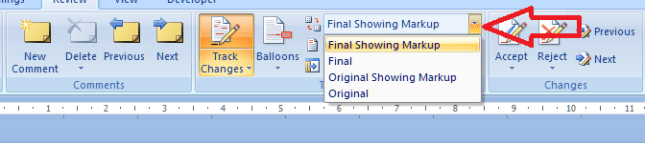
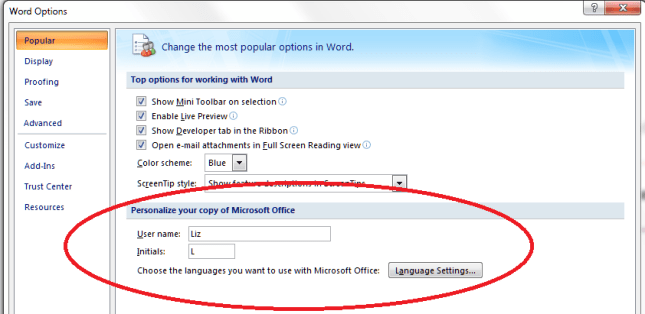
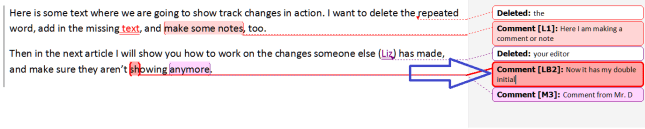
If you are amending a Word document or perhaps working on a document with someone else (a colleague or an editor), it is sometimes useful to be able to highlight some of the text in order to point it out to your collaborator.
Here are three useful ways to highlight text in Word … and one TERRIBLE way that you will never think of using once you’ve read and digested this article.
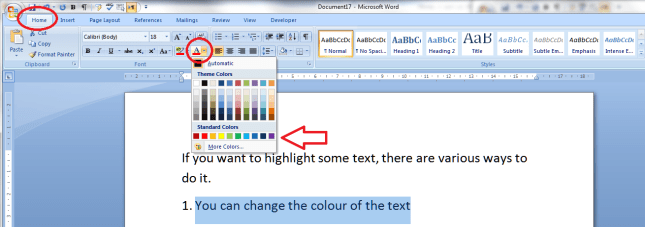
How to highlight text by changing its colour
This can be useful if you want to mark text you want to change, edit, delete, expand, etc.
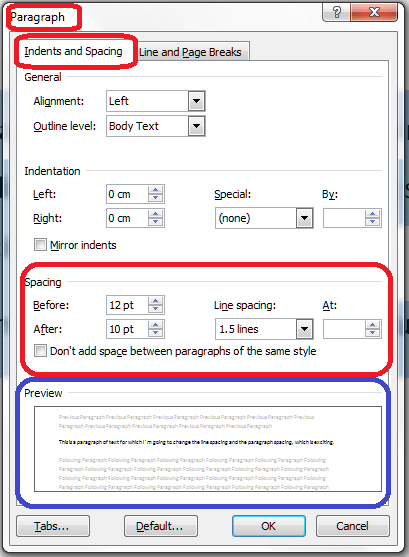
Make sure you’re in the Home tab and the Font section. Highlight the text you want to change and click on the Change Text Colour button:
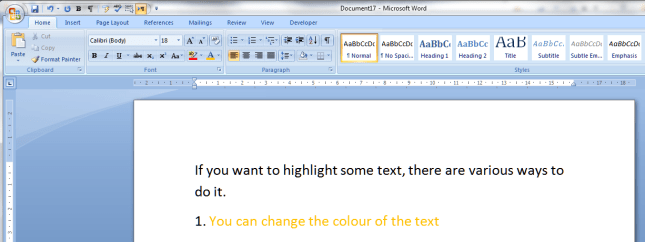
Choose the colour you want your text to be, and click on it. Hey presto:
This can be useful but there is a limited range of colours that are a) legible on a white background and b) sufficiently distinguishable from black. This can be particularly problematic for a reader with a visual impairment or colour blindness.
So you might want to think about using the next option …
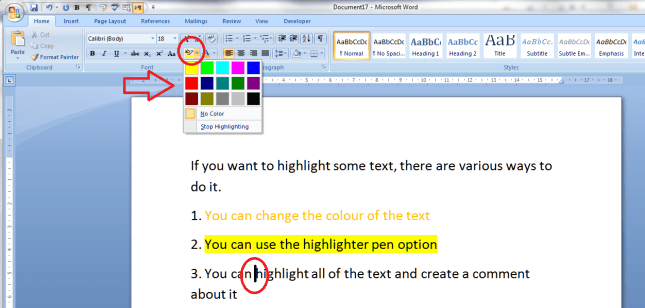
How to highlight text using the “highlighter pen”
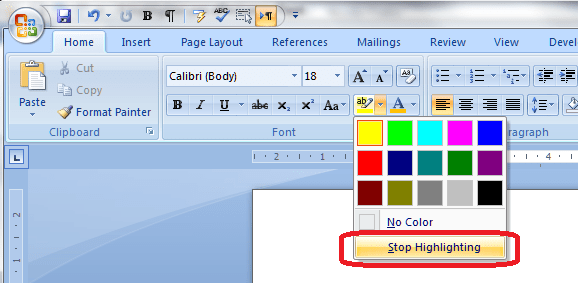
Just like in real life, you can scribble all over your document using a highlighter pen!. Again, you will find the Highlighter Pen button in the Home tab, Font section, next to the Change Text Colour button. You can use this in two ways:
1. Highlight your text first, then click on the button and choose a colour:
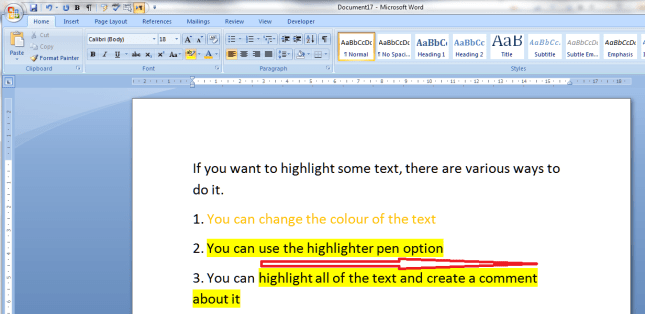
The text you had highlighted will now appear in black with the background colour you selected:
2. Place your cursor anywhere on the page and click the Highlighter Pen button. Your mouse pointer (which usually looks like a capital I unless you’ve changed it) will change to look like a pen. (Unfortunately this does now show up on a screen print. If anyone can find me a copyright-free image of this cursor change, please let me know!)
Left click where you want to start and run the mouse pointer/pen along the text you want to highlight:
The text will become highlighted as you run the pen along. Note, though, that if you use this option, your mouse pointer will keep on acting like a highlighter pen until you click back on the Highlighter Pen button and choose Stop Highlighting:
This is all great if you just want to mark, say, chunks of text that you’ve changed so your editor can see what they need to recheck. But if you need to make any comments on that text, pay very close attention to the two methods coming up and make sure you choose the correct one!
How to highlight and comment on text the CORRECT WAY
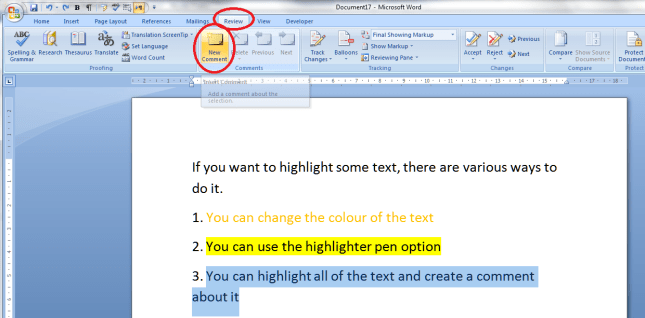
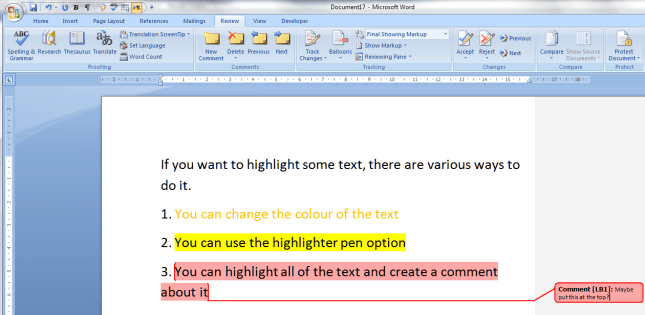
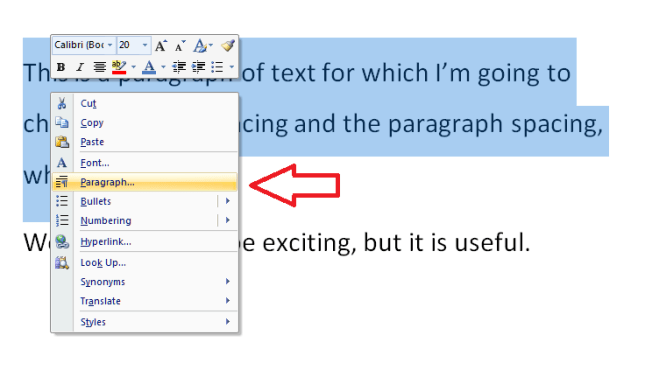
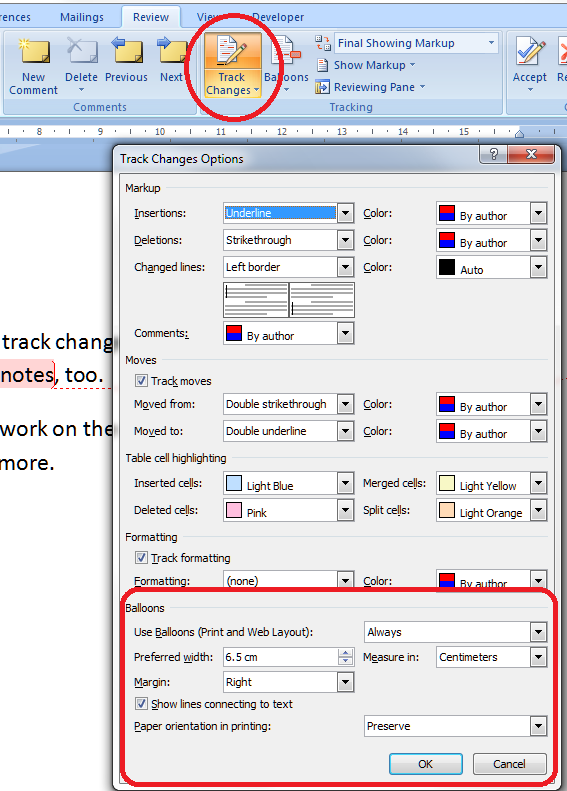
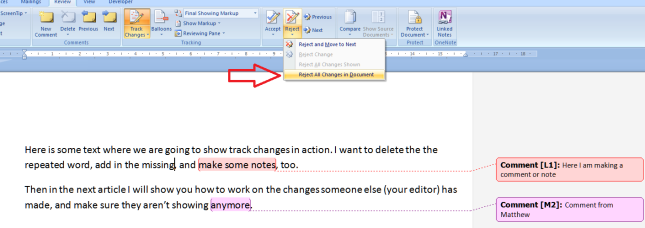
If you want to comment on some text, the correct way to do it is this. Highlight the text and in the Review tab, Comments area, click on New Comment:
A comment balloon will appear, and you can type your comment inside the balloon. If your collaborator wants to comment back, they can just add a new comment in a new balloon, and so it goes on.
The joys of using this method are twofold:
1. You can skip through the comments using the Next Comment button and you’ll never miss one.
2. You can delete the comments you’ve dealt with, the highlighting will automatically disappear, and you’ll be left with a nice tidy document.
If you’re working with someone on a document and you want to draw their attention to something and make a comment, this way we’ve just seen is the way to do it.
How to highlight and comment on text the WRONG way
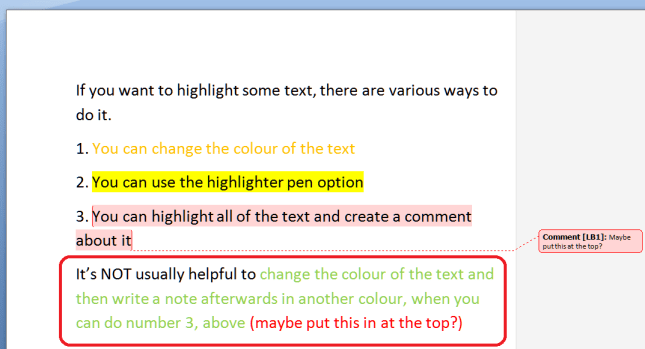
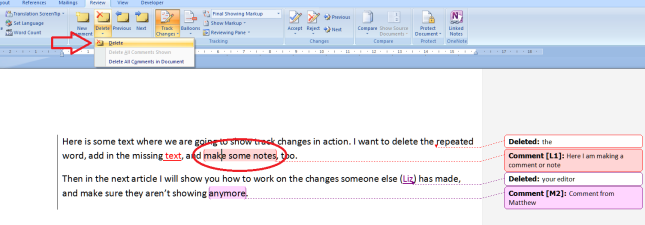
Please, don’t do this. If there’s a lovely, neat way to add comments to a document, which there is (see above), there is no need to write your comments within the text itself, like this:
If you receive a document marked up like this, for each instance of a comment from your collaborator, you’re going to need to change the colour back to normal, delete the comment, or maybe add one of your own. No skipping lightly from comment to comment, but a grim stare at the document to spot the issues.
You can learn more about using Track Changes and Comments in other posts on this blog. Please don’t be tempted to try this method at home!
So, in this article we have learned how to highlight text in three good and one bad way. I hope you’ve found this useful.
If you have found this article useful, please share it using the buttons below, and leave me a comment!
This is part of my series on how to avoid time-consuming “short cuts” and use Word in the right way to maximise your time and improve the look of your documents.
Please note, these hints work with versions of Microsoft Word currently in use – Word 2003, Word 2007 and Word 2010, all for PC. Mac compatible versions of Word should have similar options. Always save a copy of your document before manipulating it. I bear no responsibility for any pickles you might get yourself into!
Find all the short cuts here …