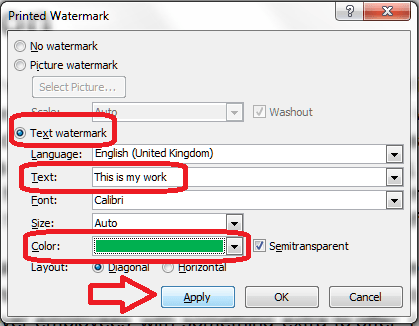
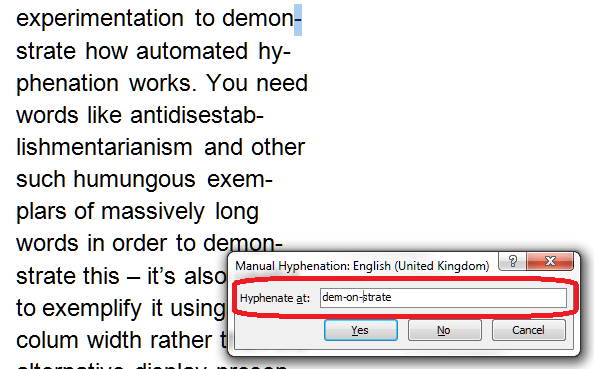
As part of my series on protecting your document, which has looked at Applying Watermarks and Protecting Word 2010 Documents, today we’re going to look at the features for protecting your document offered by Word 2007.
Why would I want to protect a document?
We covered this in more detail in the post on Word 2010, but in summary, it’s useful to be able to protect your documents because …
- You can stop the wrong people from opening the document (including if you’re sending it via email etc.)
- You can stop the wrong people from editing the document (protecting what you’ve written and/or changed)
Where is the menu for protecting documents in Word 2007?
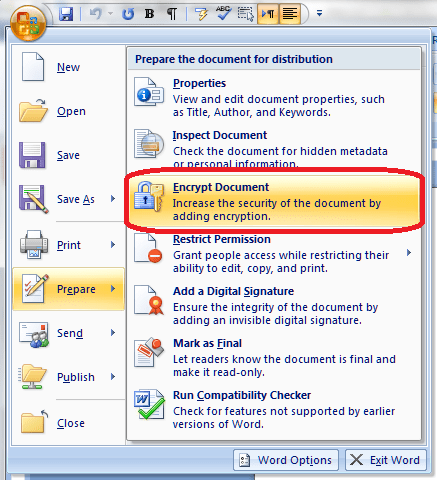
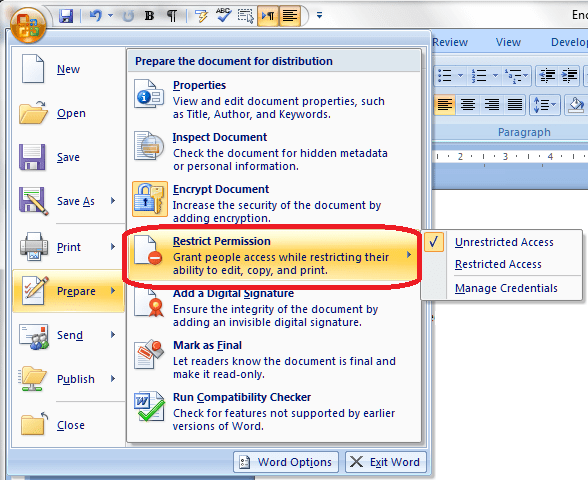
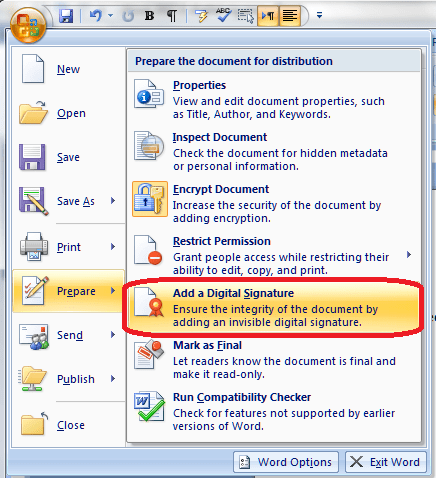
You will find the menu for protecting documents under the Start button at the extreme top left of your screen. Once you’ve clicked on the round button, you will see a menu starting with New, Open …
Click on Prepare and you are given a menu to do with preparing the document to be sent, protecting it, and editing its properties:
How do I add a password to a Word 2007 document?
The most simple way to protect a document is to add password protection. This means that no one without the password can open it (so if you email it to someone, it can’t be intercepted and opened, or people who aren’t meant to see confidential information can’t open a confidential document).
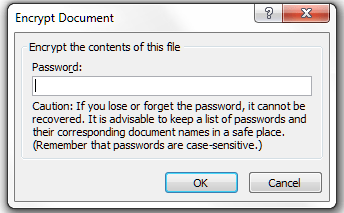
Go to the Encrypt Document entry on the menu and click on it:
You will then be asked to enter a password (twice). Do remember this, and remember to share it with anyone else who might be permitted to open and read it.
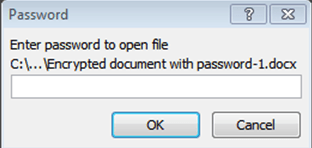
This is what happens when you or anyone else tries to open the file:
How do I make a Word 2007 document read-only?
Another way to protect your document from unwanted edits is to make it read-only. Of course, anyone can “save as” the document and make all the changes they want, but your original document, with its file name, is protected, and often people don’t realise that they can save as, anyway.
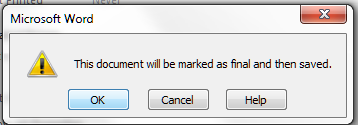
To do this, select the Mark as Final entry from the menu:
Now, when someone opens this document, they will be told that it is read-only and they cannot edit it.
How do I restrict editing in a Word 2007 document?
Another option is to restrict certain types of editing in your document.
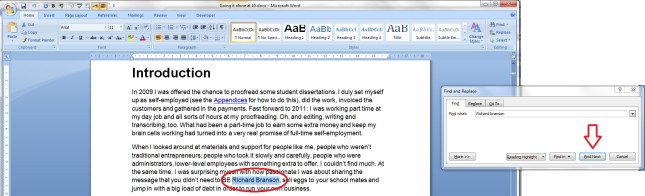
Confusingly, this is in a different area of the menus to the rest of the protection features. You will need to go to the Review tab, then the Protect section, which consists of a single button marked Protect Document. Click on the button itself or, if you must, the little arrow at the bottom right of that button (this has exactly the same effect. Why did they add that little arrow? Who knows!) to bring up the menu:
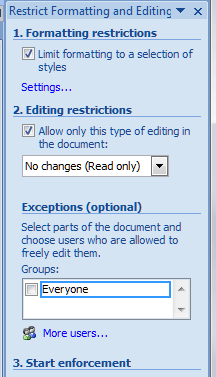
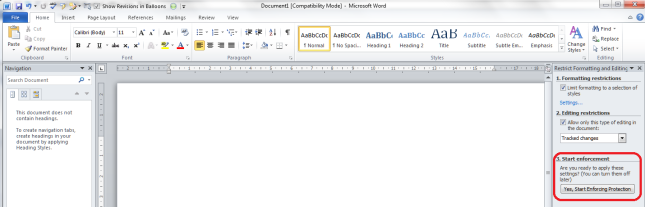
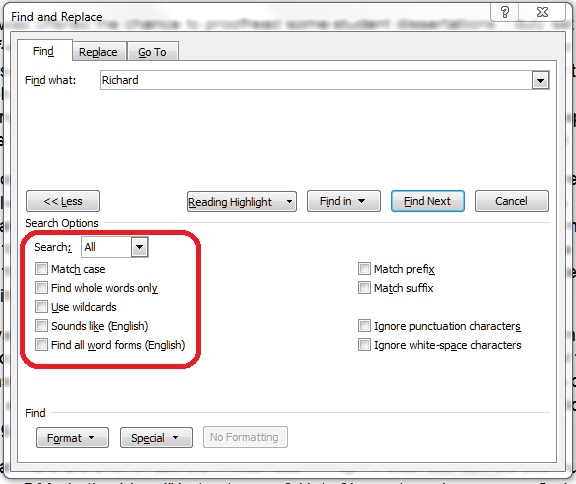
Click on Restrict Formatting and Editing to be given a list of options: Formatting restrictions, Editing restrictions and Start enforcement:
Formatting restrictions
This option allows you to select what formatting other people can apply to the document (you will want to do this after you have done all your own formatting to make sure that you can do what you want to do). Click on the tick box and then Settings to choose what formatting can be changed:
You are given a dialogue box with lots of different options. Note that you can allow the AutoFormat to override the formatting restrictions if you want to. But this is where you can choose what can be amended and what cannot be amended. This is particularly useful if you want to ensure that the Headings Styles that you’ve carefully set up will stay the same in the document.
Editing restrictions
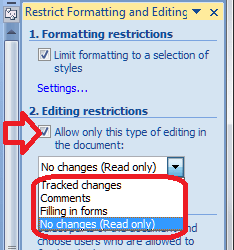
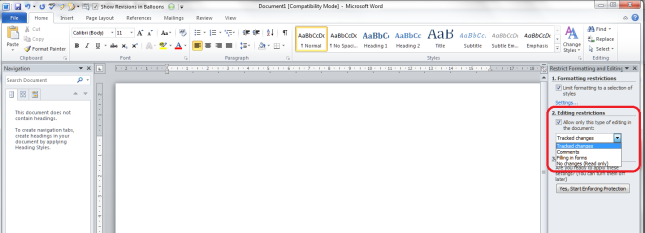
You can edit what changes other users can make to your document in terms of textual changes, too. Have a look at the Editing restrictions section, tick the tick-box, and drop down the menu to see the options:
Editing restrictions allow you to choose whether the document becomes Read only or will allow tracked changed editing only or adding comments or filling in forms. Some of my clients make the documents that they send me tracked changes only so they can see exactly what I change in their documents. It’s a good way to remind people to keep Track Changes on if you’re working together collaboratively. Filling in forms is useful if you want people to fill in your form but not change the actual form.
Restricting editors
It is possible to restrict the ability to make changes to certain people if you’re working in a multi-user, networked environment:
These permissions can be restricted to individual editors; however, see the next section for details on this option, as it needs to run alongside other network options that you may or may not be using..
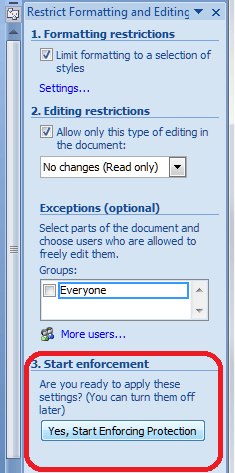
Start enforcement
When you want to put these restriction in place, click on the Start enforcement button that appeared as soon as you click or change anything:
How do I add individual editing permissions to a Word 2007 document?
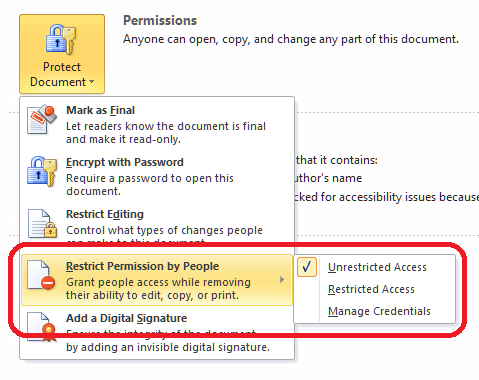
The Restrict Permission part of the original menu we’ve been talking about, under the top left button and Prepare, allows you to add individual editing permissions to your document (this can also be accessed in the Review – Protect menu as discussed in the section above):
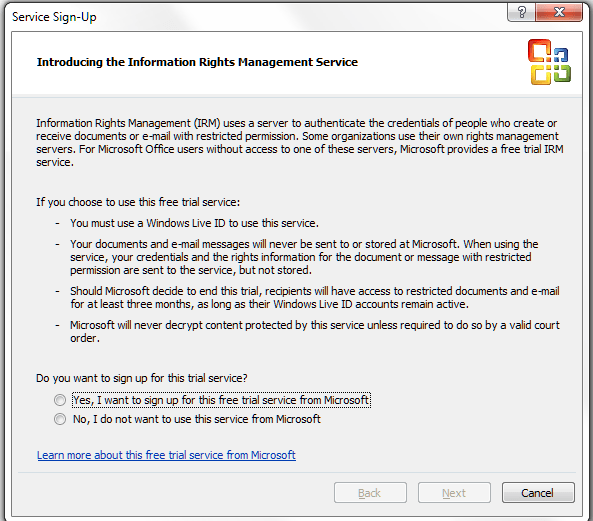
This is a Windows option that allows you to set permissions for different people, and is usually used within an organisation. You need to use Microsoft’s Information Rights Management Service alongside it and be signed up to Windows Live. The message that comes up if you click Restricted Access or Manage Credentials explains in more detail:
Most larger organisations have rights management systems that inform their procedures and file/drive setups, and these will usually allow you to set permissions and protect your document in that way. As this is outside the scope of this article: you will need to talk to your administrator or IT support department.
But this option is here for you to use, and can be done if you have the relevant signups.
Be careful: Contact IT or your systems administrator before signing up for something that can affect access to documents on a shared organisational system.
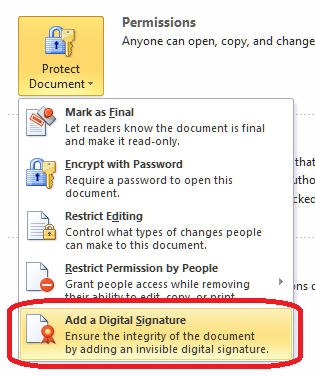
How do I add a digital signature to a Word 2007 document?
Adding a digital signature to a Word document can protect it to an extent and mark it as yours, plus an increasing number of companies request this if they’re signing you up to their pool of contractors, etc. Once again we’re in Start button – Prepare territory – this time we want the Add a Digital Signature section:
In order to use this feature, you need to purchase a signature service from the Office Marketplace, as Word will tell you if you click on this option:
Alternatively, you can sign up to a third-party digital signature service which will apply your digital signature to documents via an uploading and downloading service.
How do I print to PDF using Word 2007?
Making a Word document into a PDF is still the best way to protect it. A PDF is like an image of the document that can’t be edited, a bit like a photocopy or a picture taken of it.
Unlike with Word 2010, you can’t actually print direct to PDF using Word 2007. If you want to turn Word 2007 document into PDFs, you will need to download a PDF printer such as Adobe or CutePDF Writer.
Once you have got a PDF writing program installed, you can “Print” to PDF by hitting the Print button as usual then selecting your PDF writer as the “printer”:
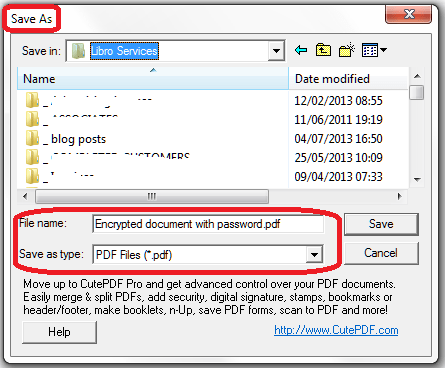
Once you’ve pressed OK, you will then be asked to choose a filename and a path under which to save the document:
Note that, as in the above picture, you can password protect your PDF at this stage. This is a good idea, as software is now available that will let people edit PDFs, something that was not previously easy to do. We’ll talk more about using PDFs to protect your document in the next article.
In this article, we’ve learnt how to use the features of Word 2007 to protect your document, using passwords, read-only status, editing restrictions, permissions and digital signatures.
———————
This is part of my series on how to avoid time-consuming “short cuts” and use Word in the right way to maximise your time and improve the look of your documents.
Related posts:
Protecting Word 2010 Documents
(coming soon)
Protecting your document using PDF
Please note, these hints work with versions of Microsoft Word currently in use – Word 2003, Word 2007 and Word 2010, all for PC. Mac compatible versions of Word should have similar options. Always save a copy of your document before manipulating it. I bear no responsibility for any pickles you might get yourself into!
Find all the short cuts here …