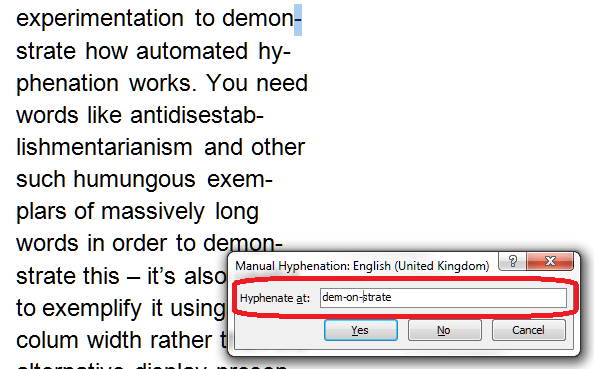
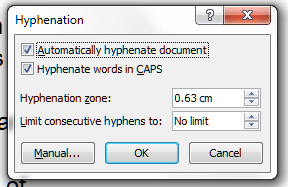
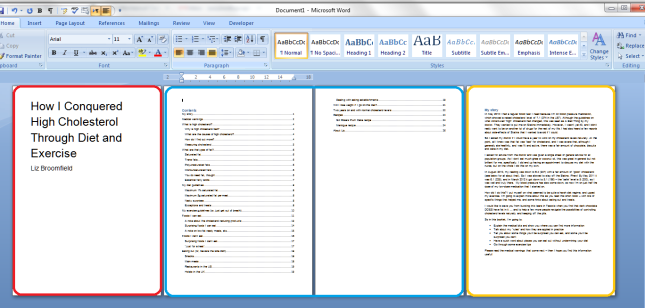
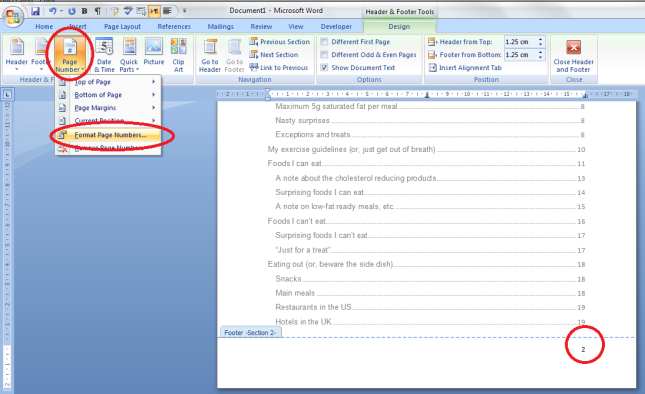
I came across Tammy Salyer via Twitter and was so intrigued by the fact that she’s both an editor and a creative writer that I asked her to write a guest post for me about how this works for her. Read on to find out how she uses her “editor’s brain” (the ‘dreaditor’) to help her fiction writing …
We all know that voice. The one in our head that says, “My Godiva, woman, did you really just string five adjectives in a row to describe your character’s appearance?” Or, “What-what-what!? You do know that dangling modifier makes you sound like a complete goon, right?” We’ll call that voice “The Dreaditor”—the evil, amorphous being that skulks within the crevasses of our brains and tries at every turn to squash our creative voice into so much jumble-y pulp.
For a lot of writers, the inner editor is worse than having Spock after he’s downed ten cups of coffee quoting bad lines from Star Trek directly into our ears in a bid to create order out of our creative chaos. “Are you sure it isn’t time for a colourful metaphor?” ~ Spock,”The Voyage Home” Or, “Nowhere am I so desperately needed as among a shipload of illogical humans.” ~ Spock, “I, Mudd”).
When starting out, many of us have to work very hard to ignore that voice, which can be exhausting and stifling to our creative brains. However, in contrast to the common notion that writers must completely turn off the Dreaditor, especially in their first draft, and just let fly with whatever mental ejecta our brainmeats conjure, I’ve found incalculable benefits in my eight years of serious writing to merging the personalities of Dreaditor and writer. By bringing these two personas together, I’ve learned how to stop the Dreaditor from yucking my yum and keep the writer within from being lost down the rabbit hole of endless possibility. Let me share these benefits with you.
First, the Dreaditor does a wonderful job of helping me figure out what I’m really trying to say. It is a master at clarifying ideas and making sentences get right to the point before they get out of hand.
We’ve all done it; a brilliant idea flashes through our creative brain and we start rapping at the keyboard as if the poor tool were Hungry, Hungry, Hippo. Finally, 300 words later, we type in a period. Then reality hits. We’ve just summarized our protagonist’s inner struggle with his addiction to chocolate milk in the most babbling run-on sentence known to humankind. Already we’re loath to think about what we’re going to have to go through in the second draft to figure out what we were trying to say in the first place, then to tighten up that sentence so our readers can figure out what the heck we’re talking about. But having a well-developed Dreaditor act as a kind of babelfish by automatically taking those potentially long and quirky sentences and distilling them into writing that is both concise and comprehensible the first go round barely slows your stream-of-consciousness writing a whit.
Secondly, no one is more innately compelled to pursue the elegance of structure as an editor, and thinking with your editor brain as you create helps you write toward a stronger overall story structure sooner. It’s one thing to be writing a fabulous scene that’s going to blow your villain into a new dimension—literally—but if your story is a romance set in the Old West, this may not be the most productive use of your time (no matter how fun it is). Having part of your brain always focused on how your writing links to your story arc and anchor scenes, how best to develop your characters in all situations, and what elements of the world you’ve built can be tied into your plot and conflict keeps your forward momentum more consistent in the long run. It also mitigates the pain later of having to cut wonderfully fabulous scenes, which you’ve sweat blood over, because they just don’t fit.
The third and most obvious benefit to having the Dreaditor always on duty is the vast amounts of time and mental energy you will save on your rewrites and subsequent drafts. An editor generally values efficiency in both language and movement toward an end goal. Being diligent about keeping your writing as streamlined and error-free as possible from the outset comes in immensely handy when deadlines loom. Additionally, it saves having to make endless passes at a particular page or scene if you’ve approached it with the precision-targeting focus of an editor from the beginning.
What works for me is certainly not a universally better process for all writers. However, I can honestly say that my writing began to improve in leaps after I’d taken a few self-editing classes. Becoming a successful creative writer is a subjective path with a variety of different objectives, depending on each person’s desires. Yet, becoming a writer with polished self-editing skills can only serve to propel every author closer to whatever their personal writing goals are. Plus, how many of us haven’t secretly wanted to be that person at parties that snootily points out to others that they’ve erroneously used “which” when “whose” is the correct word?
What do you think? Does every fiction writer have a dreaditor? Can you edit as you go along? Can a good fiction writer be a good editor and vice versa? (I know I’m not good at true creative writing, although I can write marketing copy with the best of them, and I know plenty of writers who say they couldn’t edit someone else’s work).
Author bio:
Tammy Salyer is a professional writer and editor who believes the imagination is humankind’s sixth sense. Contract of Defiance is the first book in her military science fiction Spectras Arise trilogy and was released to acclaim in Spring 2012. The followup, Contract of Betrayal, came out in February. Stop by Inspired Ink Editing, her blog, or follow her on Twitter and say hi.
I did a return guest post on Tammy’s blog with ten top tips for fiction writers. Read it here!