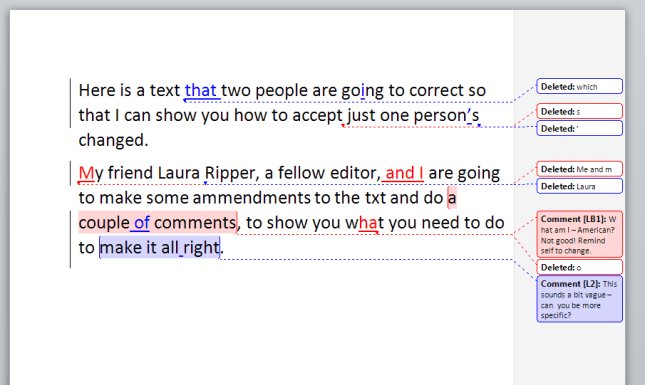
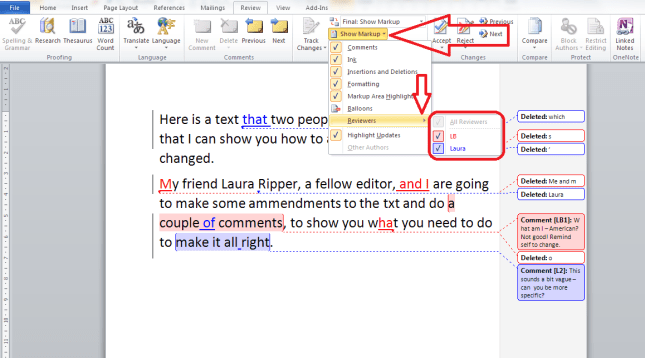
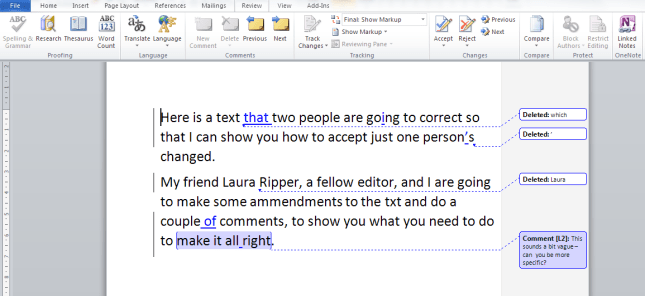
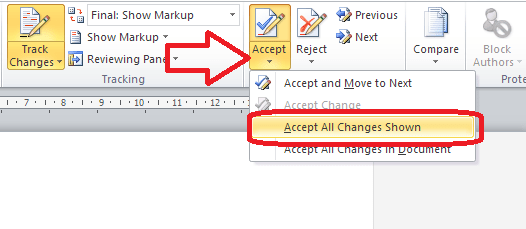
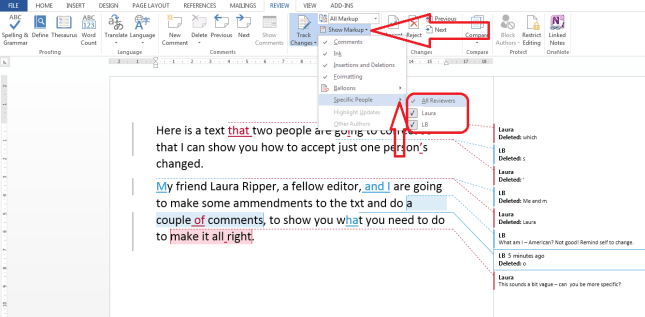
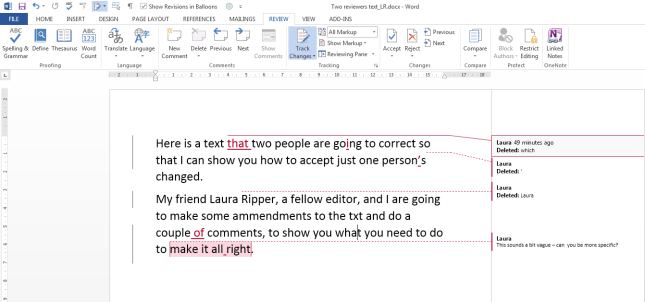
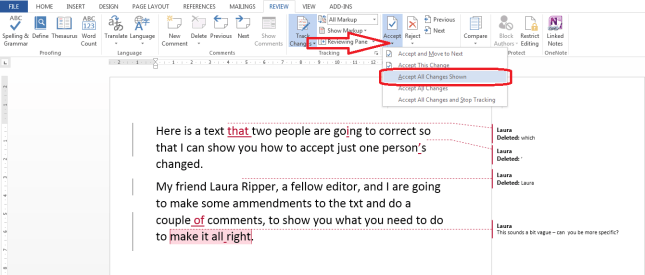
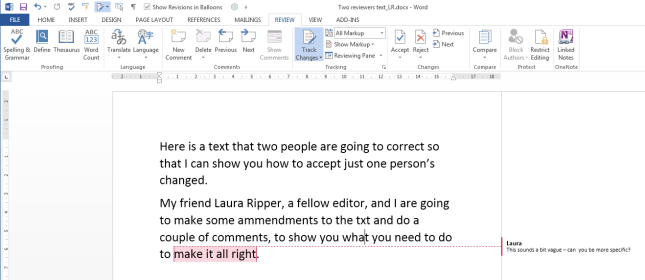
Because transcription is usually paid by the audio minute (i.e. if you have a 20 minute tape, you will be paid 20 x your per-minute rate), the faster (and more accurately) you transcribe, the more money you can make per hour. Here are some tips from my own experience about how you can transcribe more quickly. It’s not all about typing faster, either – it’s about typing faster and typing smarter and working smarter.
All links are to my own articles that explain the topics in greater depth.
Typing faster
One main way (but not the only way) to improve your transcription speed is to simply (ha!) type more quickly. Here are some tips on how to build your typing speed. The first one might surprise you ..
- Number one tip: trim your fingernails.
I have studied this (because someone has to) and I can improve my typing speed by about 5% by trimming my nails. I can type more quickly when just the pads of my fingers are striking the keys. It also takes longer to wear the letters off your keys if you’ve not got long nails to scratch them …
- If you’re serious about going into transcription, especially if you have a specialised medical or legal background where the fees are that bit higher, it’s worth investing in typing training – have a look at Pitman courses.
- A decent keyboard will also help you to type more quickly. Have a look at my post on ergonomics and keyboards, as I cover that there in a lot of detail. But typing on a decent keyboard as opposed to bashing away at a laptop or netbook will improve your typing speed.
- The more you type, the faster you’ll typically get, up to a point. So you might start off a bit slow, but your speed should pick up, if you’re touch-typing reasonably accurately.
Typing smarter
As well as physically typing faster, you can use technology to help you to transcribe more quickly and efficiently.
- If you’re not using transcription management software, start doing so (read more on this here). This doesn’t do your typing for you, but it allows you to manage the speed of your tape and stop and start it in the most ergonomic way possible.
- Use autocorrect to your advantage. I’ve written about this at length in another article, but these are the most important points for building speed and accuracy:
- Set up common shortcuts right from the start – bec = because, w = with, nec = necessarily, etc. Add these are you come across them.
- Set up any words you commonly misspell – you can do this when you’re spell-checking, as there’s an autocorrect option in the spell check dialogue box (I have trouble typing occurred correctly, for example).
- As soon as you recognise commonly used words or phrases in your particular tape, get them into the autocorrect. Long album titles? The name of a big exhibition the artist is working on? Moisturiser and concealer in a set of interviews assessing makeup? If they come up more than twice, create an autocorrect for them.
- If you’re typing the names of people in the conversation, have a convention, e.g. aa for the interviewer, bb for the first interviewee, change the autocorrected text for that shortcut for each tape (e.g. aa might be Interviewer for one tape, Manager for another, Anita for a third, bb might be Interviewee, Employee or Jane), and always use the same shortcut for the main and secondary person, so it’s super-easy to remember what to type.
- How about using voice recognition software? This has got a way to go, and editing it, in my experience, takes as long as transcribing in the first place.
Working smarter
This is mainly around the things that delay you in doing the work – looking things up and distractions.
- I look things up when I’m transcribing – band names, place names, etc. It’s far more professional to provide a transcription with the facts checked and anything you can’t hear or are unsure of marked. Make looking things up work the way you need it to:
- I find it easist to look them up as I go along, you might finid that disturbs the flow. Do what’s best for you.
- I have found from experience that if I can’t hear a word, especially a technical term or proper noun, often the interviewer will ask the interviewee to spell it out … just after I’ve spent ages looking it up. So let the tape run a bit and see if it helps you pick that information up without spending time searching for it.
- I type for an hour at the very most, as after that length of time my posture droops and my typing slows. It might only be a stretch and a march up and down the stairs, but do break it up a bit. Read more about ergonomics here.
- I do need to have the Internet turned on while transcribing, because I need to look things up, but I’m careful not to answer phone calls or even look at emails until my break. Nothing is that urgent it can’t wait, and three minutes spent looking at something, plus the time it takes to get back in the transcription zone, can lose a few minutes per hour of transcribing. It all builds up!
A final thought
I hope these tips have helped to give you some ideas about how to transcribe more quickly and efficiently. Here are two final thoughts …
- If you’re reading this and you’re a journalist or researcher, not a professional typist, especially if you can’t touch type, it’s probably a better idea for you to explore finding a transcriber to do it for you than to try to get faster. I can often transcribe a tape up to twice as fast as a non-professional, freeing my clients up to do their real jobs!
- However quickly you type, ALWAYS assume a job is going to take slightly longer than you think. Why do you think this is being posted on Thursday morning instead of Wednesday afternoon …?
If you’ve found this article useful OR if you have more tips for transcribing more quickly, please do comment below – I always love to hear from my readers! There are sharing buttons there, too, so you can share this on whatever social media platforms you use. Thank you!
Other useful articles on this blog
How do you start a career in transcription? – are you suited for it?
The professional transcriber – the technology you need
10 top tips for transcribers – what every new transcriber needs to know
Why do you need human transcribers, anyway? – I explain why!
Keyboards, ergonomics and RSI – the risks and keeping safe
Transcribing multiple voices – hints to make it easier
Why do transcribers charge by the audio minute? – explains it all